-
Product Management
Software Testing
Technology Consulting
-
Multi-Vendor Marketplace
Online StoreCreate an online store with unique design and features at minimal cost using our MarketAge solutionCustom MarketplaceGet a unique, scalable, and cost-effective online marketplace with minimum time to marketTelemedicine SoftwareGet a cost-efficient, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution tailored to your facility's requirementsChat AppGet a customizable chat solution to connect users across multiple apps and platformsCustom Booking SystemImprove your business operations and expand to new markets with our appointment booking solutionVideo ConferencingAdjust our video conferencing solution for your business needsFor EnterpriseScale, automate, and improve business processes in your enterprise with our custom software solutionsFor StartupsTurn your startup ideas into viable, value-driven, and commercially successful software solutions -
-
- Case Studies
- Blog
Choosing the Right Cloud Service: IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS
An increasing number of businesses are choosing cloud services. If you aren’t familiar with this topic, cloud computing is when hardware (servers, storage, etc.) and software are delivered over the internet.
Compared to on-premises hardware and software, cloud-based solutions such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS offer several major benefits. Let’s briefly mention these benefits in order to understand why cloud computing is so popular today.
- Scalability. On-premises solutions are rather difficult to scale, as the type of hardware needed depends on your application’s demands. If your app experiences heavy traffic, you might need to significantly upgrade on-premises hardware. This problem doesn’t exist with a cloud service, which you can quickly scale up or down with a few clicks. Cloud services are a perfect solution for handling peak loads. With cloud-based services, businesses can use whatever computing resources they need.
- Cost-effectiveness. Cloud computing removes hardware expenses, as hardware is provided by a vendor. There’s no need to buy, install, configure, and maintain servers, databases, and other components of your runtime environment. Moreover, using cloud-based solutions, you pay only for what you use, so if you don’t need extra resources you can simply scale down and not pay for them.
- Immediate availability. Cloud solutions are available as soon as you’ve paid for them, so you can start using a cloud service right away. There’s no need to install and configure hardware.
- Performance. Cloud companies equip their data centers with high-performance computing infrastructure that guarantees low network latency for your applications.
- Security. Cloud infrastructure is kept in safe data centers to ensure a top level of security. Data is backed up and can easily be recovered. Moreover, cloud vendors ensure the security of your data by using networking firewalls, encryption, and sophisticated tools for detecting cybercrime and fraud.
The advantages of cloud solutions are huge, so it stands to reason that the cloud services market is booming. According to a forecast by Gartner, the global public cloud services market is expected to reach almost $247 billion this year and grow to over $383 billion by next year.
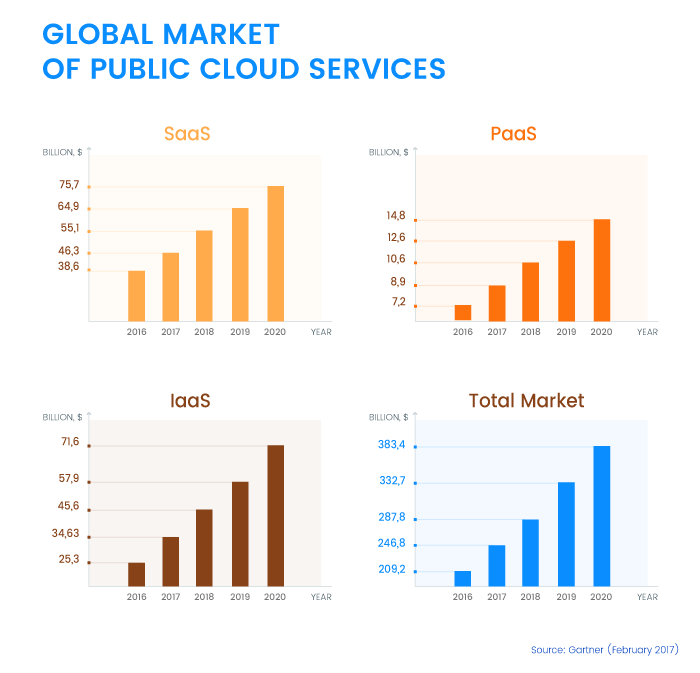
Yet choosing the right cloud service can be rather challenging. Many people have no idea what SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS mean or which of these cloud solutions they need for their projects.
We’ve written this article to explain what cloud services are available and help you choose the one that suits your business goals.
What do IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS mean?
There are three major types of cloud services: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. You’ve probably seen these abbreviations on the websites of cloud providers. Before going into details, let’s compare IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS to transportation:
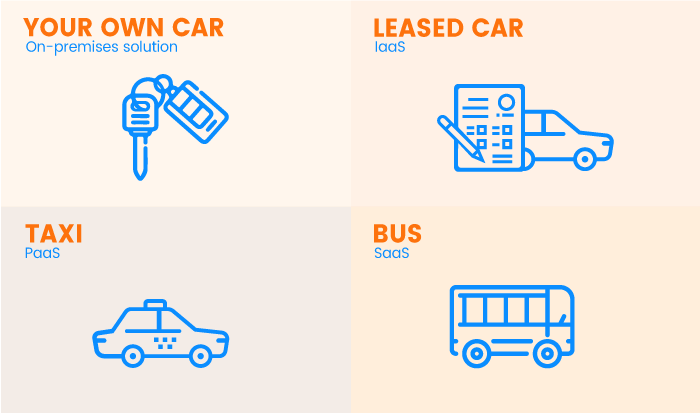
- On-premises IT infrastructure is like owning a car. When you buy a car, you’re responsible for its maintenance, and upgrading means buying a new car.
- IaaS is like leasing a car. When you lease a car, you choose the car you want and drive it wherever you wish, but the car isn’t yours. Want an upgrade? Just lease a different car!
- PaaS is like taking a taxi. You don’t drive a taxi yourself, but simply tell the driver where you need to go and relax in the back seat.
- SaaS is like going by bus. Buses have assigned routes, and you share the ride with other passengers.
These analogies will help you better understand our more detailed explanations. Let’s give a definition to each of these terms.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS allows people to use cloud-based web applications.
In fact, email services such as Gmail and Hotmail are examples of cloud-based SaaS services. Other examples of SaaS services are office tools (Office 365 and Google Docs), customer relationship management software (Salesforce), event management software (Planning Pod), and so on.
SaaS services are usually available with a pay-as-you-go (which means subscription) pricing model. All software and hardware are provided and managed by a vendor, so you don’t need to install or configure anything. The application is ready to go as soon as you get your login and password.
| Software as a Service (SaaS) | |
| Managed by you | Managed by vendor |
| – | Hosted applications |
| Development and management tools | |
| Operating system | |
| Servers and storage | |
| Networking resources | |
| Data center | |
Perfect for: end users
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS refers to cloud platforms that provide runtime environments for developing, testing, and managing applications.
Thanks to PaaS solutions, software developers can deploy applications, from simple to sophisticated, without needing all the related infrastructure (servers, databases, operating systems, development tools, etc). Examples of PaaS services are Heroku and Google App Engine.
PaaS vendors supply a complete infrastructure for application development, while developers are in charge of the code.
Just like SaaS, Platform as a Service solutions are available with a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
| Platform as a Service (PaaS) | |
| Managed by you | Managed by vendor |
| Hosted applications | |
| Development and management tools | |
| Operating system | |
| Servers and storage | |
| Networking resources | |
| Data center | |
Perfect for: software developers
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is a cloud service that provides basic computing infrastructure: servers, storage, and networking resources. In other words, IaaS is a virtual data center.
IaaS services can be used for a variety of purposes, from hosting websites to analyzing big data. Clients can install and use whatever operating systems and tools they like on the infrastructure they get. Major IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Compute Engine.
As with SaaS and PaaS, IaaS services are available on a pay-for-what-you-use model.
| Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) | |
| Managed by you | Managed by vendor |
| Hosted applications | Servers and storage |
| Development and management tools | Networking resources |
| Operating system | Data center |
Perfect for: IT administrators
As you can see, each cloud service (IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS) is tailored to the business needs of its target audience. From the technical point of view, IaaS gives you the most control but requires extensive expertise to manage the computing infrastructure, while SaaS allows you to use cloud-based applications without needing to manage the underlying infrastructure. Cloud services, thus, can be depicted as a pyramid:
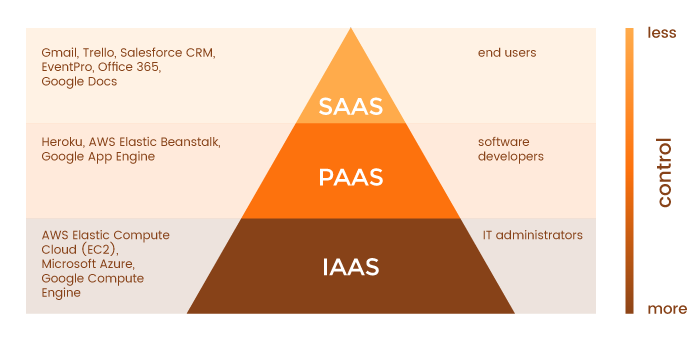
Now that you know what SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS mean, let’s be more specific about when each should be used and what their advantages and disadvantages are.
When and Why You Should Use SaaS
We’ve already mentioned some examples of SaaS solutions, so you have a general understanding of when they’re used. Let’s provide some more details.
SaaS solutions can be used for:
- Personal purposes. Millions of individuals all over the world use email services (Gmail, Hotmail, Yahoo), cloud storage services (Dropbox, Microsoft OneDrive), cloud-based file management services (Google Docs), and so on. People may not realize it, but all of these cloud services are actually SaaS services.
- Business. Companies of various sizes may use SaaS solutions such as corporate email services (Gmail is available for businesses, for example), collaboration tools (Trello), customer relationship management software (Salesforce, Zoho), event management software (EventPro, Cvent), and enterprise resource planning software (SAP S/4HANA Cloud ERP).
SaaS services offer plenty of advantages to individuals and businesses:
- Access to applications from anywhere. Unlike on-premises software, which can be accessed only from a computer (or a network) it’s installed on, SaaS solutions are cloud-based. Thus, you can access them from anywhere there’s internet access, be it your company’s office or a hotel room.
- Can be used from any device. Cloud-based SaaS services can be accessed from any computer. You only need to sign in. Many SaaS solutions have mobile apps, so they can be accessed from mobile devices as well.
- Automatic software updates. You don’t need to bother updating your SaaS software, as updates are carried out by a cloud service vendor. If there are any bugs or technical troubles, the vendor will fix them while you focus on your work instead of on software maintenance.
- Low cost. Compared to on-premises software, SaaS services are rather affordable. There’s no need to pay for the whole IT infrastructure; you pay only for the service at the scale you need. If you need extra functionality, you can always update your subscription.
- Simple adoption. SaaS services are available out-of-the-box, so adopting them is a piece of cake. We’ve already mentioned what you need to do: just sign up. It’s as simple as that. There’s no need to install anything.
Of course, SaaS solutions have certain disadvantages as well, so let’s mention a couple of them:
- You have no control over the hardware that handles your data.
- Only a vendor can manage the parameters of the software you’re using.
When and Why You Should Use PaaS
PaaS solutions are used mostly by software developers. PaaS provides an environment for developing, testing, and managing applications. PaaS is therefore the perfect choice for software development companies.
No wonder that software developers use PaaS services such as Heroku, Elastic Beanstalk (offered by Amazon Web Services), and Google App Engine.
PaaS provides a number of benefits to developers:
- Reduced development time. PaaS services allow software developers to significantly reduce development time. Server-side components of the computing infrastructure (web servers, storage, networking resources, etc.) are provided by a vendor, so development teams don’t need to configure, maintain, or update them. Instead, developers can focus on delivering projects with top speed and quality.
- Support for different programming languages. PaaS cloud services usually support multiple programming languages, giving developers an opportunity to deliver various projects, from startup MVPs to enterprise solutions, on the same platform.
- Easy collaboration for remote and distributed teams. PaaS gives enormous collaboration capabilities to remote and distributed teams. Outsourcing and freelancing are common today, and many software development teams are comprised of specialists who live in different parts of the world. PaaS services allow them to access the same software architecture from anywhere and at any time.
- High development capabilities without additional staff. PaaS provides development companies with everything they need to create applications without the necessity of hiring additional staff. All hardware and middleware is provided, maintained, and upgraded by a PaaS vendor, which means businesses don’t need staff to configure servers and databases or deploy operating systems.
Of course, PaaS cloud services have certain disadvantages:
- You have no control over the virtual machine that’s processing your data.
- PaaS solutions are less flexible than IaaS. For example, you can’t create and delete several virtual machines at a time.
When and Why You Should Use IaaS
IaaS solutions can be used for multiple purposes. Unlike SaaS and PaaS, IaaS provides hardware infrastructure that you can use in a variety of ways. It’s like having a set of tools that you can use for constructing the item you need.
Here are several scenarios when you can use IaaS:
- Website or application hosting. You can run your website or application with the help of IaaS (for example, using Elastic Compute Cloud from Amazon Web Services).
- Virtual data centers. IaaS is the best solution for building virtual data centers for large-scale enterprises that need an effective, scalable, and safe server environment.
- Data analysis. Analyzing huge amounts of data requires incredible computing power, and IaaS is the most economical way to get it. Companies use Infrastructure as a Service for data mining and analysis.
Infrastructure as a Service provides the following major advantages for businesses:
- No expenses on hardware infrastructure. IaaS vendors provide and maintain hardware infrastructure: servers, storage, and networking resources. This means that businesses don’t need to invest in expensive hardware, which is a substantial cost savings as IT hardware infrastructure is rather pricey.
- Perfect scalability. Though all cloud-based solutions are scalable, this is particularly true of Infrastructure as a Service, as additional resources are available to your application in case of higher demand. Apps can also be scaled down if demand is low.
- Reliability and security. Ensuring the safety of your data is a IaaS vendor’s responsibility. Hardware infrastructure is usually kept in specially designed data centers, and a cloud provider guarantees security of your data.
Finally, let’s specify the disadvantages of IaaS cloud solutions:
- IaaS is more expensive than SaaS or PaaS, as you in fact lease hardware infrastructure.
- All issues related to the management of a virtual machine are your responsibility.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Which Cloud Service Is Suitable for You?
It’s time to pick which cloud-based service you need. In fact, the choice totally depends on your business goals, so first of all consider what your company needs. Here are some common business needs that can easily be met with the appropriate cloud service:
- If your business needs out-of-the-box software (CRM, email, collaboration tools, etc.), choose Software as a Service.
- If your company requires a platform for building software products, pick Platform as a Service.
- If your business needs a virtual machine, opt for Infrastructure as a Service.
If you feel that you can’t make the right choice on your own, we can help you choose the most appropriate solution to meet your business goals.














