-
Product Management
Software Testing
Technology Consulting
-
Multi-Vendor Marketplace
Online StoreCreate an online store with unique design and features at minimal cost using our MarketAge solutionCustom MarketplaceGet a unique, scalable, and cost-effective online marketplace with minimum time to marketTelemedicine SoftwareGet a cost-efficient, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution tailored to your facility's requirementsChat AppGet a customizable chat solution to connect users across multiple apps and platformsCustom Booking SystemImprove your business operations and expand to new markets with our appointment booking solutionVideo ConferencingAdjust our video conferencing solution for your business needsFor EnterpriseScale, automate, and improve business processes in your enterprise with our custom software solutionsFor StartupsTurn your startup ideas into viable, value-driven, and commercially successful software solutions -
-
- Case Studies
- Blog
Telemedicine Software Explained: Types, Features & Benefits
Telemedicine has become extremely popular over the last two years due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Remote provision of medical services has become normal, and that’s not going to change when the pandemic is over. As a result, demand for telemedicine software is expected to grow dramatically in the next five years. According to EMR’s Global Telemedicine Market Outlook, the telemedicine market will reach about $173 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 24% between 2022 and 2027.
In this article, you will learn about the main telemedicine softwares functions and their benefits for both customers and medical providers. Additionally, we will review the latest telemedicine projects developed by RubyGarage to show you the practical uses of technology in the telemedicine market.
What is telemedicine software?
Telemedicine software is a desktop, mobile, or web platform for providing remote medical care, i.e. providing care when the patient and the doctor are not in the same room. It lets physicians treat patients whenever they need regardless of location and other physical limitations. Audio calls, video meetings, and in-app text messages are the most common ways to communicate via telemedicine software. As a result, patients don’t need to spend hours in waiting rooms, exposing themselves to multiple contamination risks. In this way, telemedicine technology significantly increases the convenience and safety of accessing healthcare.
How does telemedicine work?
If a medical facility offers telemedicine options, a patient only needs an internet connection and a smartphone or computer to access healthcare services. The most common types of telemedicine services include:
- Virtual appointments. A patient can arrange a virtual visit with a doctor through a phone call, text chat, or video conference.
- Patient portal. A patient can access their medical records, communicate with doctors and nurses via messages, request prescription refills, and set up appointments virtually. In this case, doctor visits remain on-site, while patients can make all the arrangements from home.
These two services can also be combined into a single platform depending on the breadth of telemedicine services a medical facility covers.
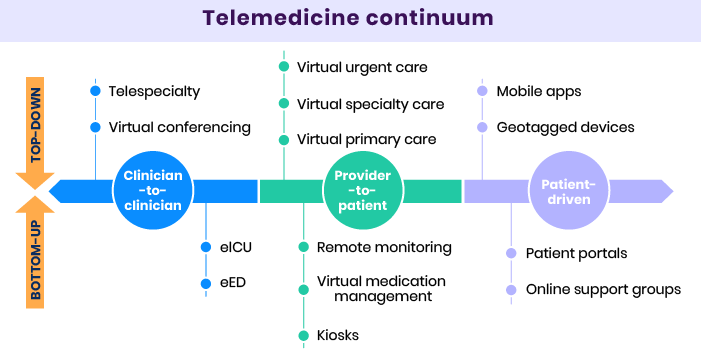
The number of telemedicine applications is growing. Here are a few examples of how telemedicine is used today:
- Routine follow-up visits. Visits that do not require on-site diagnostics are held online to save the patient’s time and increase medical practice efficiency.
- Chronic disease management. Telemedicine provides a less expensive and simpler way for chronically ill patients to control their health.
- Preventive care support. Assistance with nutrition plans, weight loss, smoking cessation, etc.
- School telemedicine. When children become ill at school, telemedicine services help assess the case urgency and provide instructions to parents without the children needing to visit an urgent care center.
- Post-hospitalization care. Telemedicine helps reduce hospital readmissions by providing remote patient guidance after hospital discharge.
- Assisted living center support. On-call doctors and nurses help determine if hospitalization is required without visiting a facility.
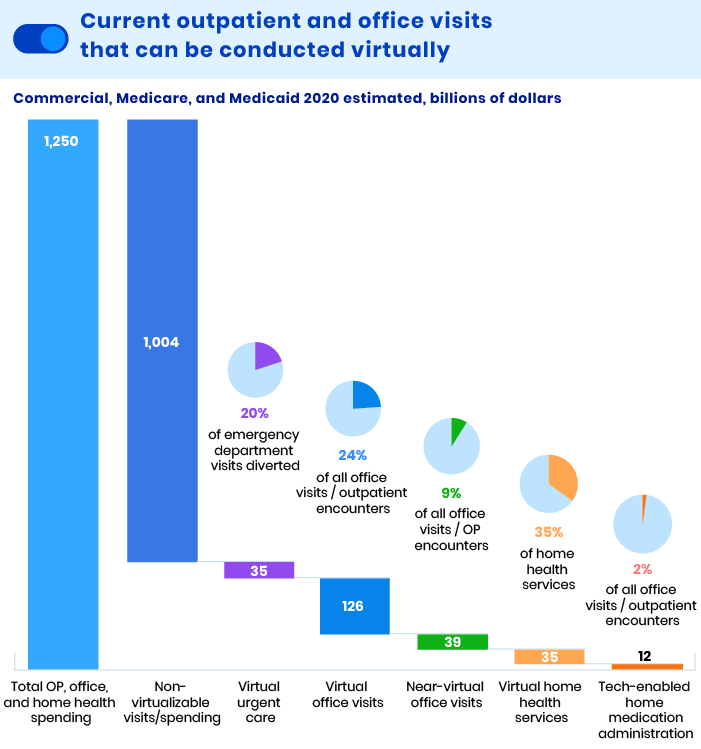
The latest McKinsey Telehealth report points out that telemedicine use has increased by 38 times compared to the pre-COVID-19 baseline in the USA. In addition, the report overviews the share of telemedicine among all appointments in different areas of medicine (for US patients):
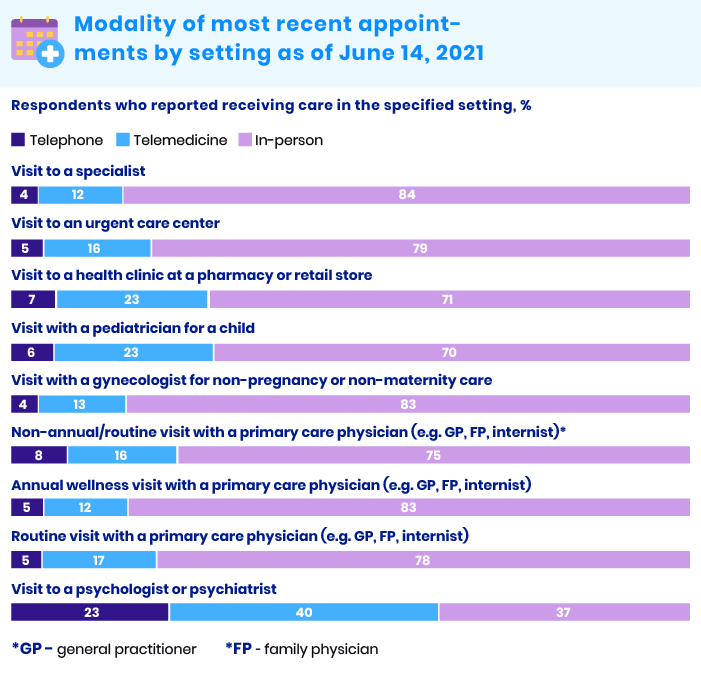
As of July 2021, telemedicine use in the USA had stabilized at a level about 38 times higher than before the COVID-19 pandemic. The telemedicine market is currently more than favorable for new entrants given the acceleration of consumer and provider adoption of telemedicine services. Now is the right time to launch new telemedicine solutions and move healthcare companies to remote services.
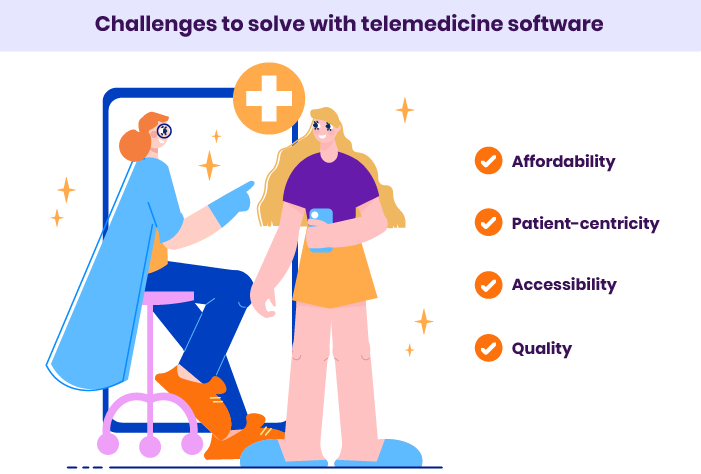
Benefits of telemedicine software
Telemedicine makes non-acute medical care significantly more convenient for patients. It also provides medical centers with a more flexible and efficient workflow. Here are the main advantages that make telemedicine softwares a win-win solution for patients and healthcare providers.
Telemedicine benefits for patients
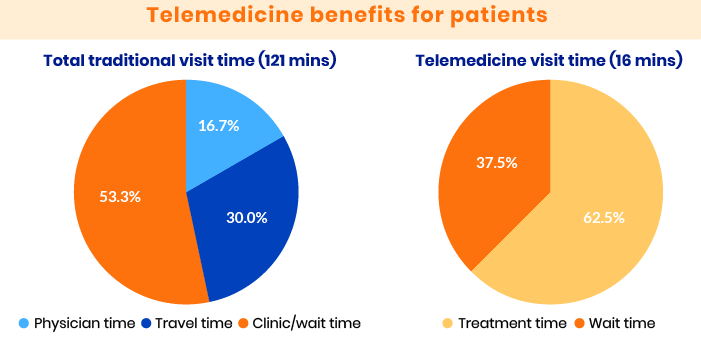
- Greater accessibility of medical care. Patients can get medical assistance when it’s hard or impossible to arrange an on-site visit (overloaded admission units, nighttime, no available specialist in the local hospital, etc.).
- Less time to get assistance. Scheduling a doctor’s appointment often takes weeks or even months for a non-urgent patient. The wait time for the same appointment through a telemedicine platform can be a few hours or days.
- No travel expenses. Patients don’t need to spend time and money traveling to a hospital or clinic, so there’s no need to take time off work.
- Lower cost. Virtual medical guidance costs less than an in-office visit. More and more medical insurance plans include telemedicine services, and these plans are also more affordable.
- Privacy. All interactions with the hospital and personnel are kept private, as there’s no need to visit a doctor’s office.
- Minimized contamination risks. There’s no need to sit in waiting rooms among other potentially contagious patients.
Telemedicine benefits for providers
- Increased revenue. With telemedicine, each specialist can see more patients within the same period. When insurers start massively reimbursing for telemedicine, providers can increase revenue without adding personnel.
- Reduced operating costs. Online appointments require no office space or office staff and take significantly less time per patient.
- Flexibility for staff. E-health solutions significantly reduce hospital bureaucracy, letting doctors focus on treatment and automating most routine operations like billing and managing medical records.
- Improved office efficiency. Hospitals can move patients who don’t require in-house therapy and diagnostics to remote care. This way, they can prevent personnel from being overworked and getting burned out, optimize their workloads, and accept more patients.
- Higher competitiveness. Medical institutions offering telemedicine services can take patients during quarantine. They are not restricted by a patient’s location and other limitations, making them more competitive.
- Fewer missed appointments and cancellations. Virtual appointments are not affected by an inability to travel to the hospital, inability to take time off work, and other circumstances.
Types of telemedicine software products
Currently, there are three major types of telemedicine software products:
- Remote patient monitoring (RPM). This type of software monitors patients from home through a range of medical devices (heart rate and pressure monitors, glucose meters, caloric intake tools, etc.). Data from connected devices is recorded in the platform. Physicians can monitor their patients online to control their conditions, monitor therapy, and detect symptoms to prevent serious health problems.
- Store-and-forward. This type of software collects and analyzes patients’ medical records. It helps patients and physicians share medical data with healthcare specialists who can provide a proper diagnosis and consultation. Store-and-forward software is widely used in radiology, dermatology, pathology, and other areas of medicine where the number of specialists can be limited. These platforms store vital sign information and patient history in text, photos, and videos, providing email, phone, chat, and video calls to communicate between patients and doctors.
- Real-time telemedicine. Such platforms provide remote interaction with healthcare providers in real time. Patients can consult doctors via phone calls, text chat rooms, or online video conferences. Regardless of the chosen technology, real-time telemedicine software allows doctors and patients to communicate as if they were in the doctor’s office. A patient’s medical history is stored in the app, and both the doctor and the patient can access it to discuss it, form a diagnosis, and make necessary changes.
The telemedicine software we've described above is primarily used to connect patients and doctors virtually. Yet there is one more type of solution – facility-based telemedicine software. Such systems connect medical providers from different facilities for accurate diagnostics and therapy.
Many platforms offer hybrid functionality. A single system can combine all the above types of telemedicine services based on the product intent.
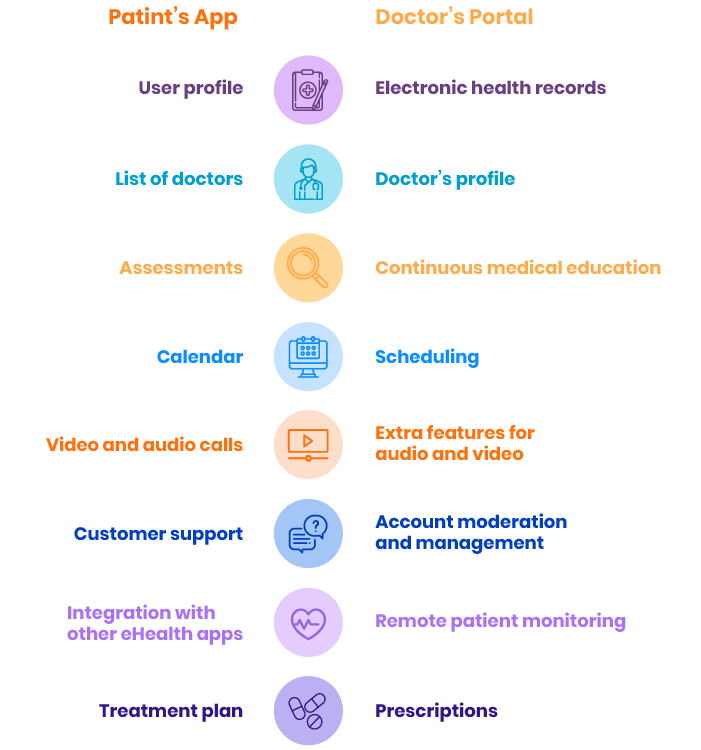
Core features of telemedicine apps
Telemedicine platforms are developed for multiple user roles. Usually, these are patients, doctors, and administrators.
Registration & sign-in
eHealth platform providers tend to make their products as user-friendly as possible. Yet you should find a compromise between usability and security. For this purpose, one-click registration with two-factor authentication is favorable. Patients can register an account via email, phone number, Google, or Facebook. Two-factor authentication is usually available via email or SMS.
Profile management
Users and doctors need to fill in their personal information and some required documents for the service. A user’s profile should also display the user’s appointment history, upcoming appointments, payments, and other activities within the platform.
EMR and EHR integration
The most important documents for a patient are an electronic health record (EHR) and electronic medical record (EMR). According to HIPAA requirements, third parties are prohibited from accessing a patient’s EMR and EHR. Only the owner and doctors can view it. If you plan to release your telemedicine software outside the USA, make sure it complies with legal requirements and standards in your target markets.
Video and audio conferencing
Communication tools are vital features of telemedicine apps, and they primarily define an app’s convenience for both patients and doctors. A platform needs to stream real-time HD audio and video meetings and record and store them in the system. It requires a robust data compression algorithm to optimize traffic loads and storage, and streamlining data sharing is essential. Consultations often require additional tools like notes, calculators, treatment guides, and protocols. That’s why video meeting rooms need to provide all that in an easily accessible way.
Chat room
Text chat is an option for solving minor issues that do not require real-time meetings with a doctor. A chat room for a telemedicine platform needs to let users attach photos and text files and should send notifications when there are new unread messages. Therefore, it makes sense to integrate a ready-made third-party chat platform instead of developing one from scratch. For e-health products, you should consider only HIPAA-compliant live chat platforms. Twilio is a suitable option.
Scheduler
Physicians need to manage their schedules, while patients need to see available spots for planning an appointment with specialists. Again, it makes sense to integrate Google Calendar, iCalendar, or other third-party planners users are familiar with. It would be convenient to improve their standard functionality by adding available spot suggestions if the desired time has already been booked. If there are no suitable time slots with the desired specialist, the platform should also suggest another qualified physician.
ePrescribe
A doctor’s online prescription should be further shared with patients and pharmacy services. Additionally, e-health apps provide drug information, pricing, information on nearby pharmacies where medications are available, and other add-ons to make the patient’s life easier. Finally, all prescriptions need to comply with legal requirements. For example, specific categories of drugs cannot be prescribed online, requiring a patient to visit a doctor in person.
Remote patient monitoring
Collecting, storing, and reporting information from medical wearables and synced apps helps doctors remotely monitor patients with chronic conditions. This helps to prevent emergency conditions and ensures better patient care.
Online payments
Telemedicine platforms should support multiple payment gateways to let patients pay for medical services online directly in the app. Credit card, PayPal, and Stripe support are standard options. Yet, make sure to check which payment platforms are most popular in your target market.
This feature set can be expanded with a rating system and customer reviews to let patients rate physicians according to their professionalism. In addition, some telemedicine apps utilize AI-based virtual assistants to help patients speed up appointment scheduling and provide routine support. Define a list of potential features based on your target audience’s needs, monetization strategy, market trends, and available budget. In our article on how much it costs to develop an app like Doctor on Demand, we analyze the approximate cost of telemedicine platform development.
Telemedicine software: RubyGarage expertise
The healthcare sector is a priority at RubyGarage. We’ve been partnering with hospitals and private practitioners from all over the world to automate, optimize, and widen their services through innovative, customer-centered software solutions. Moreover, we develop our own telemedicine products and constantly track the latest industry changes. Check out some of the telemedicine products we’ve created.
Clinix
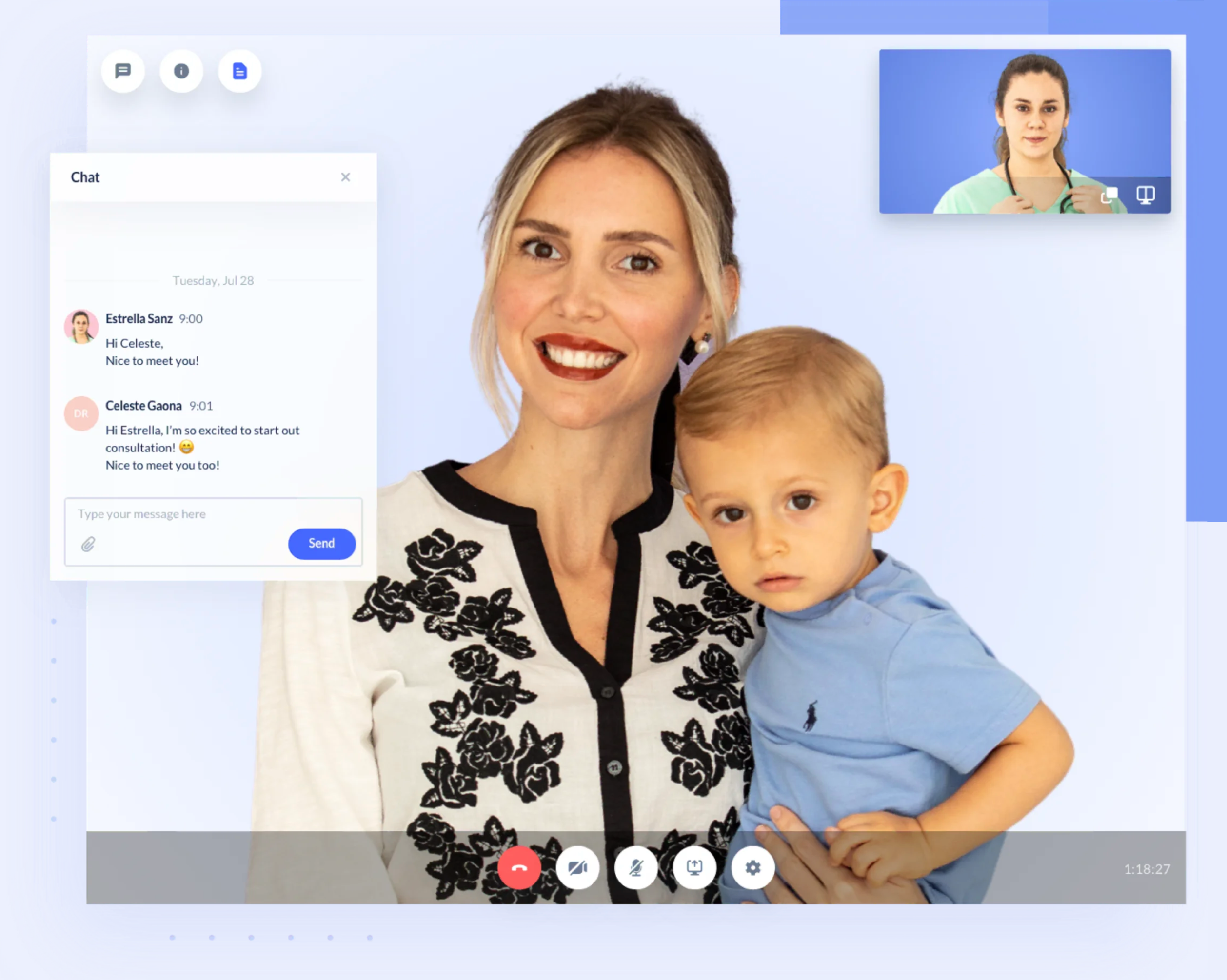
Clinix is the first telemedicine platform in Paraguay that lets patients receive remote medical assistance through video calls. Local hospitals and individual practitioners use it to consult with patients, manage their medical records, and write prescriptions online.
The RubyGarage team implemented this project from scratch, starting with comprehensive telemedicine market research to identify customers’ and hospitals’ needs. Our goal was to build a solution that would work effectively for both parties. As a result, we developed a web application for doctors and medical institutions to deliver medical care to patients and a mobile app for patients to consult with doctors and receive prescriptions online. In addition, the web and mobile apps are fully synchronized and provide safe and comfortable 24/7 access to telemedicine services.
Clinix helped Paraguayan patients receive timely medical assistance during the pandemic. The project is still ongoing, and we are extending the product’s feature set.
ExpertBox
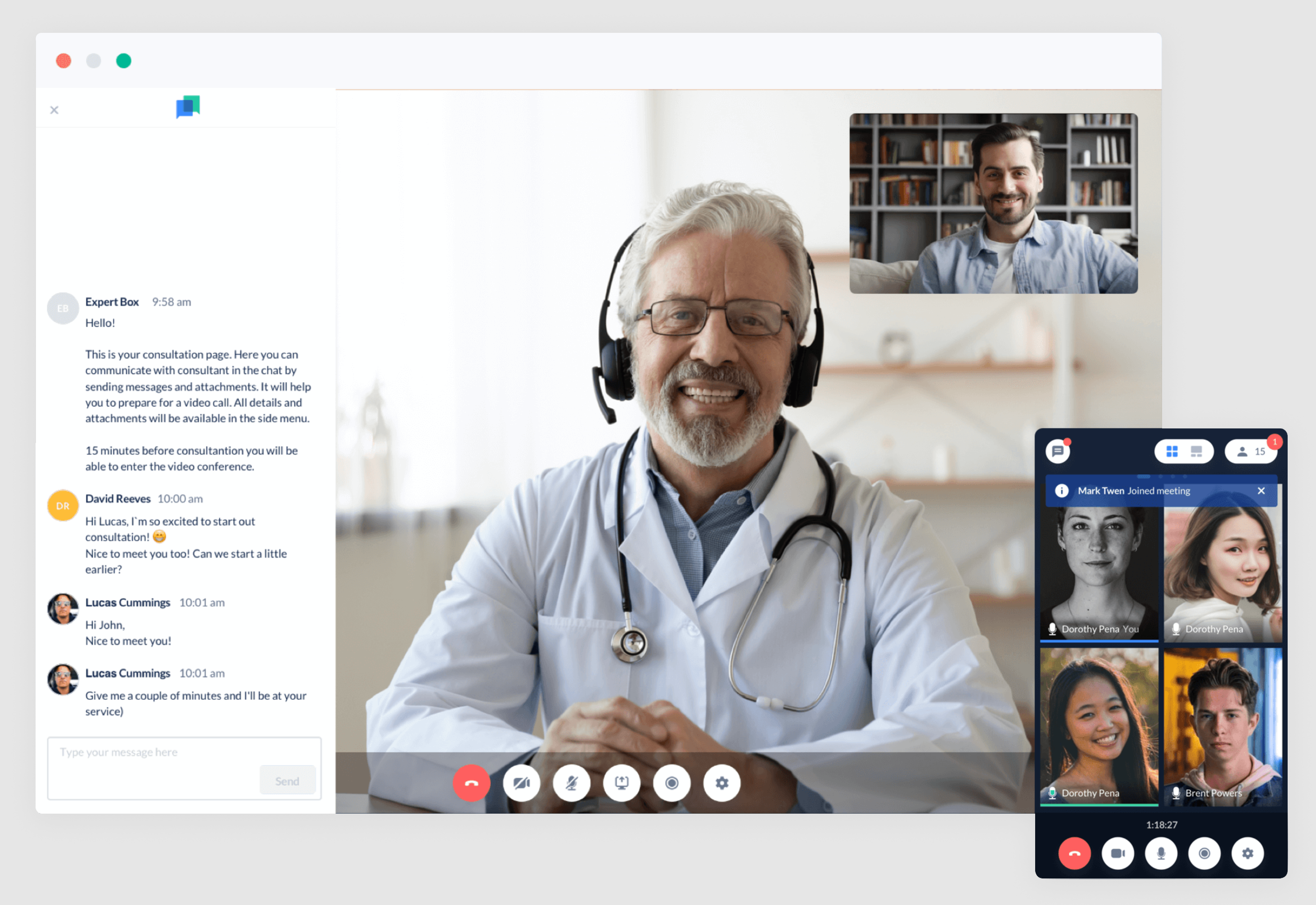
ExpertBox is our own in-house product we are proud of. We created this all-in-one video conferencing software to make remote customer interactions convenient, safe, and effective. ExpertBox has become popular for telemedicine, coaching, recruiting, law, fitness, and other consultancy services. ExpertBox features include :
- Meeting scheduling system
- HD video conferencing
- Video recording
- Chat
- In-app payments
- Staff productivity tracker
ExpertBox is HIPAA-compliant, which makes it suitable for clinics, physicians, psychologists, and other healthcare professionals to use to securely consult with patients online.
Health Marketplace
Telemedicine software covers much more than providing medical guidance. Our client requested to continue the development of their Health Marketplace startup, a platform for fitness and health practitioners to consult with clients online. Our goal was to develop a production version and implement a range of new feature upgrades.
We conducted a code audit to detect existing issues and security vulnerabilities, fix them, and prepare the platform for the following upgrades. Our next goals were to make the web platform responsive so it would display and function correctly on mobile devices and develop an iOS app.
We also developed custom marketplace and e-store functionality for web and mobile apps. In addition, we integrated a few third-party add-ons for online payments and text chat features. As a result, Health Marketplace has become a reliable, multifunctional telemedicine platform with scalable infrastructure for further upgrades.
Final Thoughts
The telemedicine industry is currently on a considerable rise. Customers and healthcare providers have already appraised its benefits in harsh pandemic conditions. More and more people are getting interested in using remote medical services. Nevertheless, gaps in technology and regulations still expose new market entrants to the risks of launching a non-viable or poorly competitive product. To minimize such risks, make sure your software development provider has in-depth experience designing telemedicine products and knows all the ins and outs of this niche.
RubyGarage offers a complete range of telemedicine software development services to help startups launch competitive products empowered by a well-thought-out, result-oriented business strategy. Let’s get in touch.
FAQ
-
Despite both terms are often used as if they meant the same, technically telemedicine is a subcategory of telehealth. Telehealth also includes non-clinical uses like self-monitoring, medical education, fitness and dietary guidance, etc.
-
Telemedicine provides benefits for all parties. Patients get the opportunity to receive care remotely, with no need to visit the doctor’s office. Healthcare providers can help more patients in less time and operation cost. The healthcare system benefits from optimized clinics operation, wider access to medical services, and their decreased self-cost.
-
The latest studies reveal active interest to telemedicine software from both customers and healthcare providers. The demand for such solutions will keep significantly growing in the following years as a natural effect of global automation and digitization trend in the healthcare industry.










