-
Product Management
Software Testing
Technology Consulting
-
Multi-Vendor Marketplace
Online StoreCreate an online store with unique design and features at minimal cost using our MarketAge solutionCustom MarketplaceGet a unique, scalable, and cost-effective online marketplace with minimum time to marketTelemedicine SoftwareGet a cost-efficient, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution tailored to your facility's requirementsChat AppGet a customizable chat solution to connect users across multiple apps and platformsCustom Booking SystemImprove your business operations and expand to new markets with our appointment booking solutionVideo ConferencingAdjust our video conferencing solution for your business needsFor EnterpriseScale, automate, and improve business processes in your enterprise with our custom software solutionsFor StartupsTurn your startup ideas into viable, value-driven, and commercially successful software solutions -
-
- Case Studies
- Blog
iOS vs Android Development: Which One is Best for Your App?
Four billion people. That’s the global digital population in 2018 according to We Are Social and Hootsuite web portal reports. And there are almost 3 billion active mobile social users. This is a market you can’t ignore. If you still don’t have a mobile app for your business, then it’s high time to get one. iOS and Android are the two major mobile operating systems nowadays. Which one should you start with when building a mobile app? iOS, Android, or perhaps both?
When comparing iOS development vs Android development processes, don’t rely on your personal preferences. Think about your business and the parameters that matter the most. Below, we’ve gathered data and compared different metrics for these two operating systems to help you make the right decision.
1. Number of users and average users of each platform
When starting any project, you first need to think about the customers who will use your product. To make your app work, you have to know exactly who your target audience is, where these people live, what income they have, and what platform they prefer. We’ve collected all the latest data on iOS and Android users below.
Market share
As we all know, there’s only one manufacturer that produces devices for iOS: Apple. But there are thousands of small and large companies that make devices for Android. This competition lowers prices, leading to a market flooded with cheap Android phones, tablets, and other gadgets. Low prices have given Android the lion’s share of the market. Statcounter has released a chart that reflects this situation.
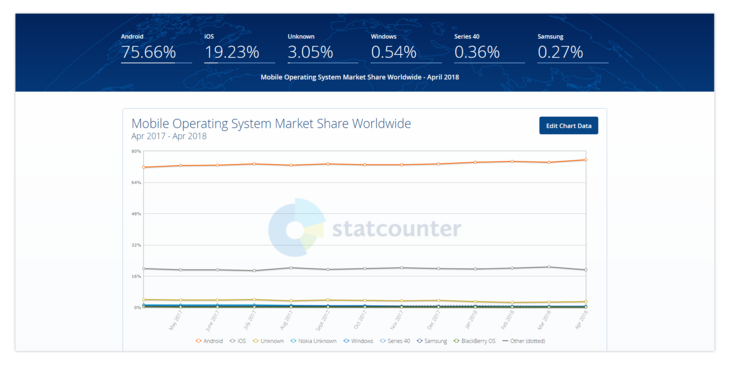
As you can see, worldwide about 75 percent of people use Android and only 19 percent use iOS. Android is the undoubted winner. Yet don’t make any hasty decisions, as we’ve only started this Android development vs iOS battle!
Latest operating system version
The number of customers who use the latest version of each operating system is also very important – especially if you want to repeat the success of the IKEA app with its VR objects or the Sephora app that’s known for its AI chatbot. All this fancy functionality requires the most modern hardware and the latest operating system versions.
Unfortunately, not all of your customers will be able to try these features. iOS updates automatically and doesn’t require any effort from a user, while Android updates are optional and require user input. The result of this can be seen in the charts below.
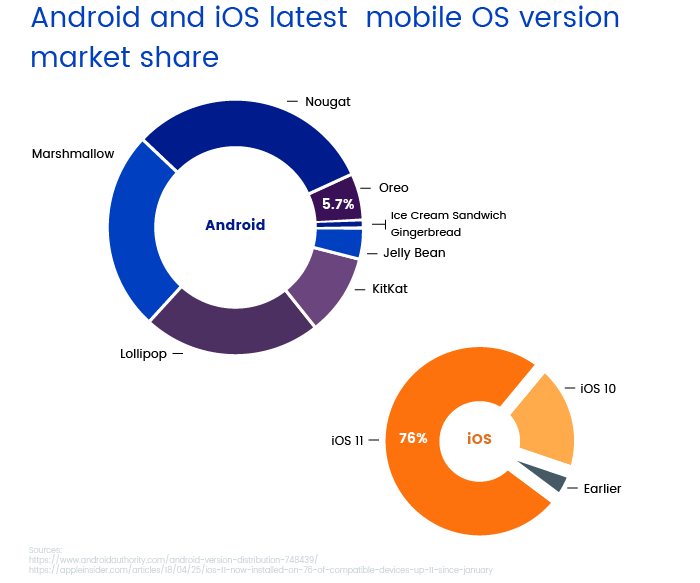
As of the second quarter of 2018, only 5.7 percent of all Android owners are running the latest Oreo version of Android. In contrast, 76 percent of iPhone owners are running iOS 11, the latest version of the operating system.
User loyalty
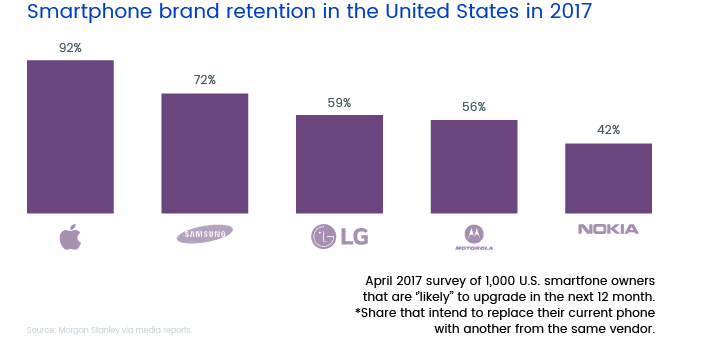
User loyalty is another vital metric to track when comparing Android development vs iOS development. Studies show that iPhone owners are much more loyal to their phone’s manufacturer than are Android owners. Ninety-two percent of iPhone owners say they wouldn’t buy a device from a different manufacturer. Among Samsung owners, 77 percent make this claim; for LG, it’s 59 percent, and for Motorola, 56 percent.
User demographics
The regions you want to reach with your app can be crucial in making your choice. If you aren’t targeting your app at a global audience but instead at a smaller geographic area, make sure you choose the most popular platform for that area. Below is a map to give you more insights on platform preferences across the globe.
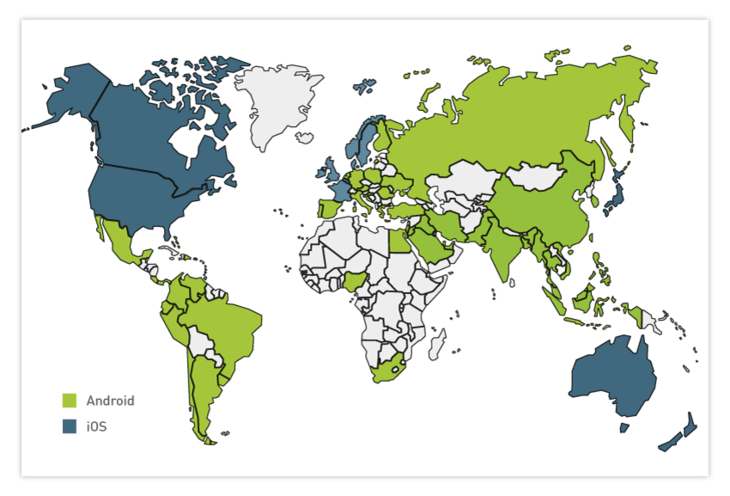
This map shows that a lot of European, South American, Asian, and African countries prefer Android. Certain countries with higher incomes, including the US, some European countries, and Australia prefer iOS. These regional preferences can partially be explained by the low cost of some Android mobile phones.
On average, people who prefer iOS are younger than people who prefer Android, have a higher level of education, and earn more money.
App revenue and spending power
The average iOS owner is ready to pay more, so we shouldn’t be surprised that the Apple App Store gets more revenue from mobile apps than the Google Play Store. In 2017, the Apple App Store managed to bring in $38.5 billion compared to $20.1 for Google Play.
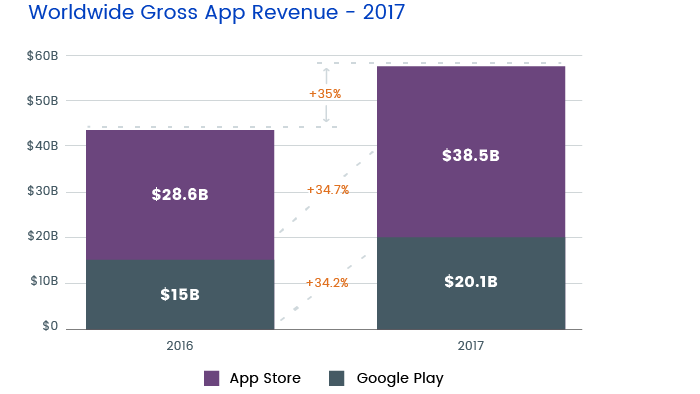
It’s also a fact that the average iOS app makes 45 percent more profit per customer than the average Android app. What’s more, 10 percent more iOS users are willing to make in-app purchases.
These are many more differences you need to know about when comparing Android app development to iOS app development. Let’s take a look at the most vital.
2. Development complexity
Of course, the main thing that influences the complexity of your mobile app is the functionality set you want. Yet the platform counts as well. Here are the main factors that define the complexity of development:
Hardware
A developer with a computer – in fact, almost any computer – can build an Android app. Linux, Windows, and even Mac devices will do the job. Developing an iOS app requires your developer to have a Mac.
Compatibility
There’s no use in choosing old technologies for modern projects. The newer Kotlin and Swift programming languages are replacing Java and Objective-C.
Here’s when compatibility questions come to the first place. Kotlin is 100 percent compatible with Java. This complete compatibility means you can use all of the numerous frameworks and libraries for Java in a Kotlin project. What’s more, you can actually switch from one programming language to the other from line to line.
With Swift, things don’t look quite as good. Objective-C and Swift aren’t completely compatible. This creates lots of issues and makes development harder. Besides, each code version has different compatibility, so one framework can be more compatible with Swift 2 than with Swift 3, for instance.
Even though the compatibility issue doesn’t affect people who are building their very first mobile app, those who already have one and want to revamp it may face certain challenges.
Code
Programming languages develop and change with time. New, updated versions are more versatile and advanced. But this creates another issue if two versions of one language are very different. This is exactly what happened to Swift, making it more difficult for developers to use it and to work with projects written in earlier versions of the language.
Device fragmentation
There are about 18 iPhone models, 14 of which are still in regular use. Speaking about Android phones, there’s an uncountable number in all shapes and sizes. This phenomenon is called device fragmentation. While developing an Android application, the product owner and developer have to choose a limited number of devices and screens that the app will definitely support. This influences the complexity and cost of development.
Additionally, there are a lot of Android operating system versions in use simultaneously, which causes another fragmentation issue. As a result, creating an app that’s compatible with all devices and operating system versions can be time-consuming and pricey.
Interface peculiarity
Apple, just like Google, wants all the apps in their stores to look native since they distribute (or sell) them and want to guarantee quality to the end user. That’s why Apple and Google have released design guidelines to encourage a unique brand look among the millions of apps in their stores. The guidelines differ, yet it’s not very difficult to follow them.
The only thing you need to remember is that Apple has very strict requirements that they check during the app publishing review process. Meanwhile, Google sticks to the main principles of Material Design yet leaves room for innovation.
3. Publishing to the app stores
The process of releasing apps to the two app stores also differs. Each app store has its own set of rules and a strict release procedure. Consider them too as they can influence the rollout time of your mobile app. Here are the main peculiarities.
Cost
To roll out an iOS app, you’ll need to pay $99 per year as an individual developer or $299 as a company. Android charges $25 only once, without any limitations as to the number of published apps.
Approval time
It usually takes a few hours for Google to approve and publish your app. In the App Store, there’s a committee of real people who check if your app follows all the guidelines and rules and only then allows (or doesn’t allow) it to roll out. In the past, this process took up to a week, but now the average App Store review time is about a day.
Staggered/phased releases
In case you aren’t sure about an update or a new version of your app and would like to test it with a small group of users, both the Play Store and App Store offer you such a chance.
Staggered release on the Play Store allows you to update your app so only a certain number of users will get the new version. You can choose the percentage of users who will get the updated app and preferred countries. If needed, you can halt and resume a staggered release. A phased release in the App Store works pretty much the same, only you can’t choose the percentage of people who will get the update – the percentage depends on the day. For instance, on the first day only 1 percent of users will get the update, on the third day 5 percent will receive it, and 100 percent will get it on the seventh day. You can also pause and resume a version update if desired.
4. Time and cost
The average time required to build iOS and Android apps is approximately the same. The main difference here lies in the testing stage. The testing process for an Android app takes more time unless the app is designed to work only with very few devices. This is caused by device fragmentation and the variety of screen sizes and configurations. To provide a high-quality product and furnish full compatibility with a maximum number of devices, a quality assurance engineer has to test an app on a number of different devices and spend a lot of time on this. As a result, there are often more bugs to fix in Android apps than in iOS applications. Correspondingly, the cost of an Android project is generally higher.
The bottom line
When considering the right mobile platform for your business, remember that every detail matters. Check the infographic below and compare the most significant metrics about iOS and Android platforms.
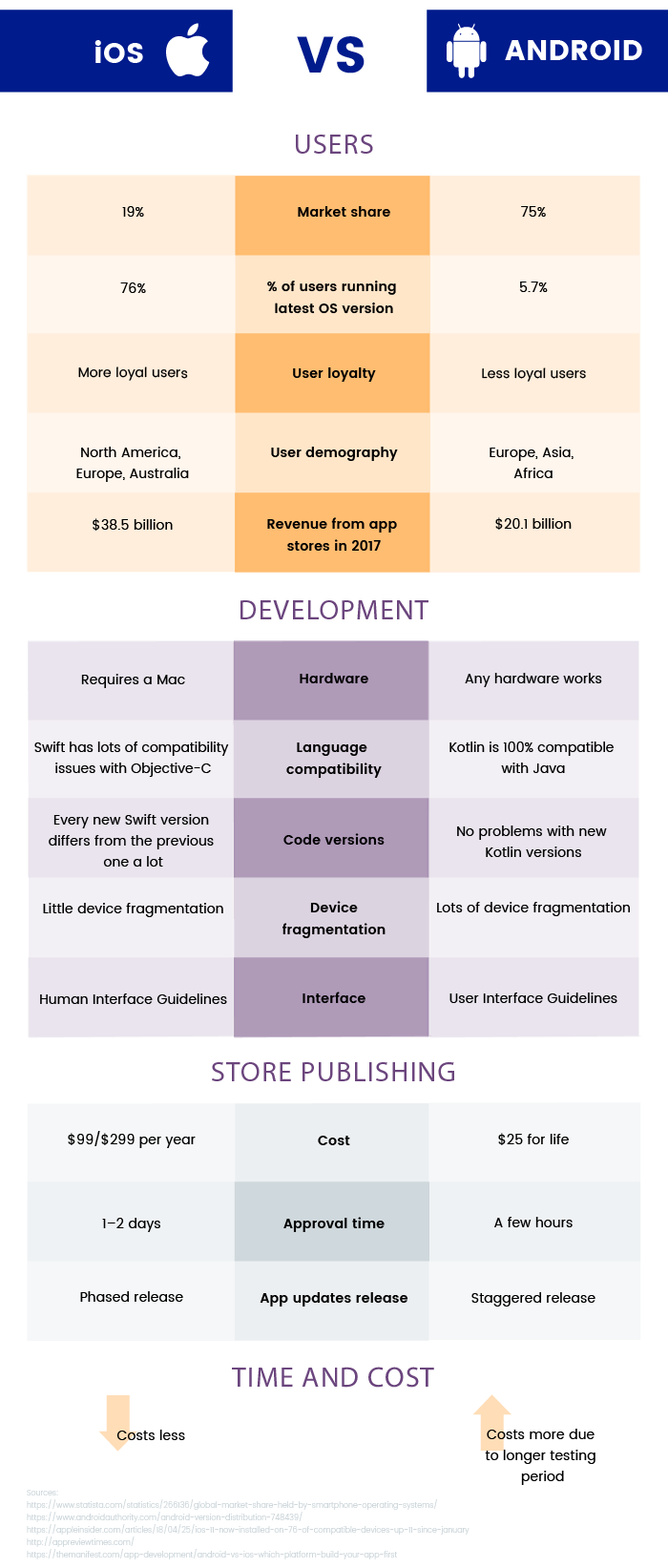
When starting to develop your own mobile application, make sure you’ve thought through one of the most important considerations – having a reliable and experienced vendor. The company you choose can make project delivery fruitful or unpleasant.